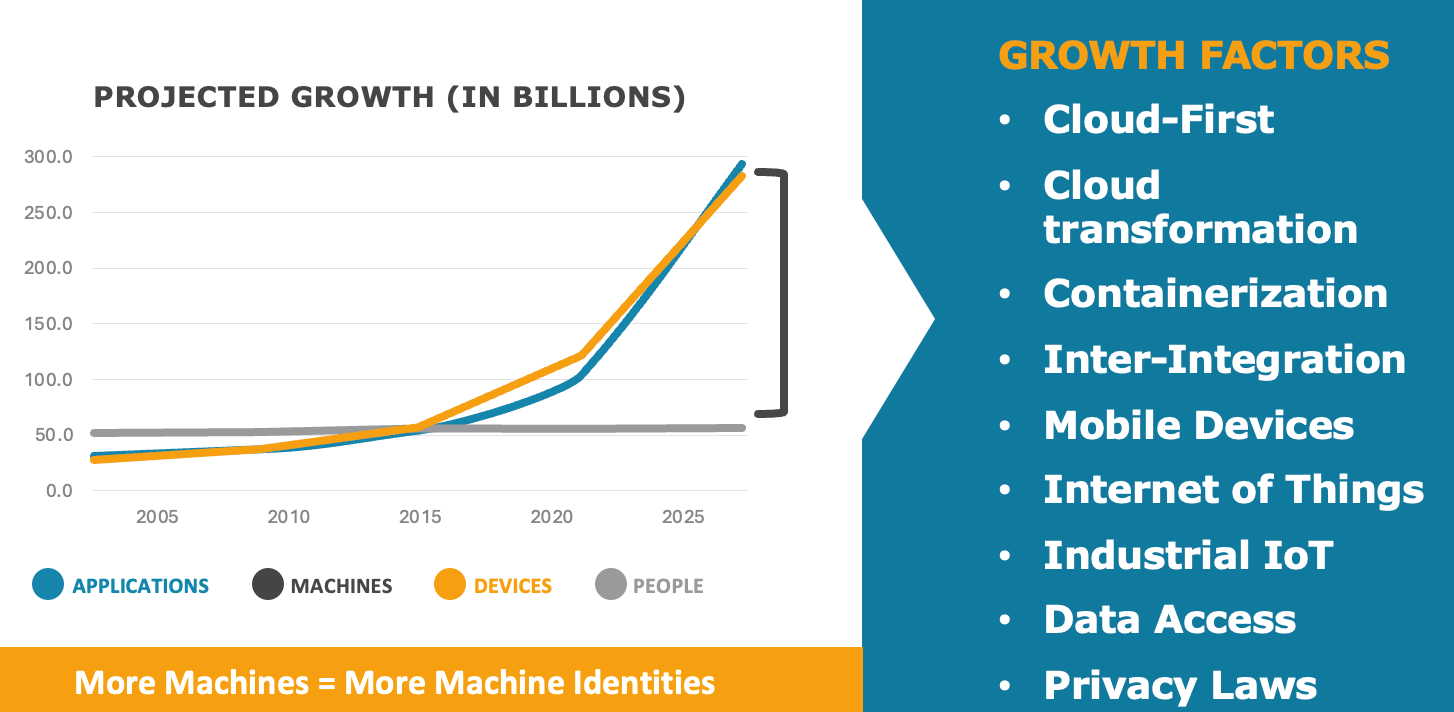
Machine Identities outnumber humans 85:1 today and are projected to grow into the billions. Further, there’s been a lot of buzz today about Machine Identities and the recent changes announced by the CA/Browser (CAB) Forum affecting SSL/TLS standards.
Here’s a quick overview of the key upcoming deadlines:
- March 15, 2026: Maximum certificate validity reduced to 200 days
- March 15, 2027: Further reduction to 100 days
- March 15, 2029: Certificates limited to 47 days, with Domain Control Validation (DCV) periods shortened to 10 days
To help you navigate these changes, we’ve answered some of the common questions we hear from our clients.
What is the CAB Forum?
The CA/Browser Forum (Certification Authority Browser Forum) was established in 2005 to strengthen internet security by developing and maintaining industry standards for digital certificates. These certificates underpin:
- SSL/TLS encryption
- Code signing
- S/MIME (email security)
The forum’s standards ensure that certificates are:
- Issued only to verified entities
- Managed securely
- Trusted by browsers and applications
What is a Digital Certificate?
A Digital Certificate is an electronic credential proving ownership of a public key. It’s a foundational element of Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) essential for secure online communication.
Digital certificates enable:
- HTTPS for secure browsing
- Identity authentication (e.g., websites, software publishers)
- Encryption of data in transit
- Integrity of communications
What do the CAB Forum changes mean for your organization?
Shorter certificate lifespans mean significantly more frequent renewals. By 2029, managing about 50,000 certificates will generate over 472,000 renewal events — each roughly taking an hour. That’s nearly 54 years of cumulative labor, which is unsustainable without automation.
Efficient TLS certificate lifecycle management becomes a strategic necessity. Automating this process is critical to scaling and maintaining security posture.
What constitutes a Machine Identity? Is it just Digital Certificates?
Machine identities encompass more than just digital certificates. They include Service accounts, cryptographic keys, SSH keys, API keys, access keys, and any digital identity assigned to applications, devices, workloads, or services. For deeper insight, check this presentation.
What Challenges are Associated with Machine Identities?
- Proliferation: Rapid growth of machine identities across apps, workloads, IoT devices, bots, and cloud services creates a sprawling, complex ecosystem that’s tough to track.
- Process Complexity: Management is often manual and error-prone, leading to inefficiencies and a reactive security posture.
- Compliance Difficulties: Lack of clear ownership, decentralized controls, inconsistent policies, and limited visibility make compliance a significant challenge.
- Security Risks: Broad access privileges, weak or shared credentials, and excessive permissions expose organizations to unauthorized access and insider threats.
What threats do machines have to your organization?
- Expanded Attack Surface: The large number of machine identities increases vulnerability points for attackers.
- Financial and Reputational Impact: Breaches or outages can disrupt customer access, causing revenue loss and eroding trust.
- Operational Disruptions: Mismanagement can lead to system outages, threatening business continuity.
- Increased Administrative Burden: Managing identities at scale leads to higher costs and resource strain on IT and security teams.
How do Machine Identities fit into my overall IAM strategy?
Machine identities should be seamlessly integrated across all facets of your Identity and Access Management (IAM) program – including Privileged Access Management (PAM), Identity Governance and Administration (IGA), Access Management (AM), and Customer Identity and Access Management (CIAM). Avoid managing them in silos. Connect with Simeio to discover best practices and tailored solutions for effective machine identity management.
What are the key components of Machine Identity Management ?
- Visibility : Discover and Identify all machine identities & Monitor the activity
- Lifecycle: How Machine identities are provisioned, credential rotated and decommissioned in your organization
- Access : Defining policy, integrations and controls on How Machine identities access or be accessed by other non-human entities including workloads and devices
FAQ
- What is the CAB Forum?
- What is a Digital Certificate?
- What do the CAB Forum changes mean for your organization?
- What constitutes a Machine Identity? Is it just Digital Certificates?
- What Challenges are Associated with Machine Identities?
- What threats do machines have to your organization?
- How do Machine Identities fit into my overall IAM strategy?
- What are the key components of Machine Identity Management?
Machine Identity Webinars
Securing Machine Identities webinar
Simeio and CyberArk dive into the critical challenges and solutions surrounding machine identity security. As machine identities outnumber human identities by a staggering margin, organizations face mounting risks from man-in-the-middle attacks, expired certificates, and fragmented security systems.
Machines, Mergers, and Missteps webinar
Explore the new landscape of identity management in manufacturing: how unified solutions bridge legacy and modern systems, restrict third-party risks, and enable rapid, compliant access for humans, machines, and contractors.


